Choosing the right PCB manufacturing machine is a critical decision for any company involved in the electronics industry, as it directly impacts both production efficiency and product quality. With the rapid advancement of technology, the range of options available can be overwhelming. Therefore, having a clear understanding of your specific needs is essential to make an informed choice. Factors such as production volume, complexity of designs, and future scalability must be carefully considered to ensure that the selected machine aligns with the business goals.
Moreover, it is important to evaluate the capabilities of different PCB manufacturing machines, including their precision, speed, and the types of materials they can process. Each project may demand different specifications, and thus the right machine should offer flexibility and adaptability to accommodate varying requirements. By thoroughly assessing these aspects, manufacturers can not only optimize their production processes but also enhance overall quality and reduce wastage.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate PCB manufacturing machine requires a strategic approach that encompasses understanding both current and future needs. By focusing on key features and operational demands, businesses can streamline their manufacturing processes and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
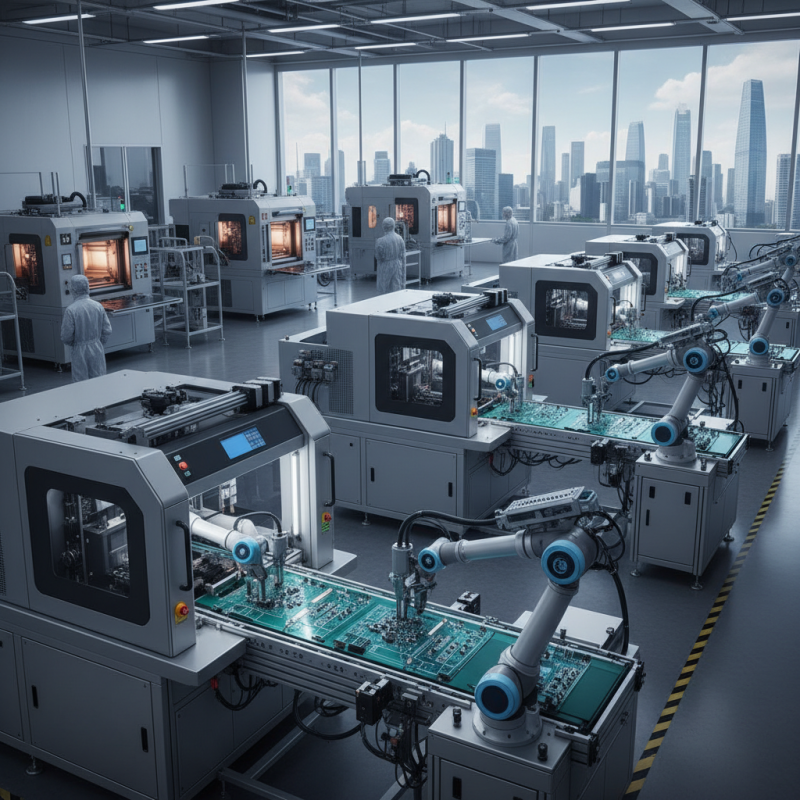

When selecting a PCB manufacturing machine, understanding the specific requirements and specifications of your projects is crucial. Begin by assessing the types of PCBs you intend to produce—single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer boards. Each type has its unique manufacturing needs, such as layer alignment precision and routing capabilities. Consider the desired production volume as well; some machines cater better to high-volume runs while others are designed for prototypes and low-volume needs.
Another important aspect is the material compatibility of the machine. Different PCBs may require various substrates, such as FR-4, polyimide, or even flexible materials. Ensure the machine you choose can handle the materials associated with your projects. Additionally, take into account the machine's automation level and ease of use. Higher automation can lead to decreased manual errors and increased throughput, but it may come with a steeper learning curve. Assessing these specifications will help ensure that your PCB manufacturing machine aligns with your production goals and quality standards.
When selecting a PCB manufacturing machine, it's essential to understand the different types available and their specific applications. There are primarily three categories of PCB manufacturing machines:
etching machines,
drilling machines, and
solder mask application machines. Each type plays a crucial role in the PCB production process and is tailored to meet various production requirements.
Etching machines are often used for removing excess copper from the laminated board to create the desired circuit patterns. They can vary in technology, with some relying on chemical processes while others use laser etching.
On the other hand, drilling machines are critical for creating accurate holes for component placement and vias in multilayer PCBs. The precision and automation levels of these drilling machines can greatly impact efficiency and the overall quality of the PCB.
Additionally, solder mask application machines are key in ensuring that the PCB's surface is protected and ensures the integrity of the electrical connections. These machines apply a layer of solder mask to enhance durability and prevent shorts between conductive traces.
Understanding these types and their applications will guide users in selecting the right machine to optimize their PCB manufacturing process effectively.
When choosing a PCB manufacturing machine, several key features are essential to meet specific needs and optimize production efficiency. First and foremost, consider the machine's capability in terms of board size and complexity. The ability to handle different sizes and types of PCBs, including multilayer configurations, will ensure versatility in your manufacturing operations. Additionally, look for machines that offer precision in drilling and routing, as well as high resolution for printing circuits. This precision directly impacts the quality and reliability of the final product.
Another critical feature to evaluate is the speed and throughput of the manufacturing process. Machines that provide fast production speeds while maintaining quality assurance allow for increased productivity and quicker turnaround times. Moreover, consider automated options for processes like soldering and assembly, which can significantly reduce labor costs and minimize human error. Lastly, user-friendly interfaces and robust software support are crucial for effective machine operation, as they enable easier monitoring, adjustments, and maintenance, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime in your PCB manufacturing process.
When assessing budget and cost-efficiency for PCB manufacturing machines, it is crucial to begin by determining your specific production needs. Evaluate the volume of production, the complexity of the PCB designs, and the types of materials you plan to use. This will allow you to identify machines that cater to your requirements without overspending. A thorough analysis of desired features, such as automated tools or multi-layer capabilities, will also affect the overall cost, so be sure to prioritize which features are essential for your projects.
Additionally, consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Look into factors such as the machine's energy consumption, maintenance needs, and the longevity of its parts. A more expensive machine that boasts lower operational costs and reduced downtime might prove to be a wiser investment in the long run. Moreover, factor in training costs for your team, as well as potential software or supply expenses, to create a comprehensive budget that reflects the true financial impact of purchasing and operating the PCB manufacturing machine.
| Machine Type | Initial Cost ($) | Operating Cost/Month ($) | Production Speed (boards/hr) | Maintenance Frequency (months) | Estimated Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level PCB Printer | 5,000 | 200 | 30 | 6 | 5 |
| Mid-Range CNC Machine | 15,000 | 350 | 50 | 4 | 7 |
| High-End Laser Cutter | 30,000 | 600 | 100 | 12 | 10 |
| Fully Automated Production Line | 100,000 | 1,500 | 200 | 3 | 15 |
When selecting a PCB manufacturing machine, evaluating the supplier's reputation and support services is crucial for ensuring a reliable partnership. According to a report by the IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries), companies that prioritize supplier reputation gain a competitive edge in the market, as a trusted manufacturer can significantly reduce production risks and improve overall quality. Supplier reviews, industry awards, and customer testimonials are essential components in assessing a potential partner’s reliability, alongside their track record in the PCB industry.
Support services play a vital role in the long-term usability of PCB manufacturing machines. A survey conducted by Electronics Supply & Manufacturing indicates that 78% of manufacturers rank after-sales support as a top factor in their purchasing decision. Effective support services include timely technical assistance, accessible training programs, and regular maintenance checks, which are critical to maximizing machine uptime and performance. Suppliers that offer comprehensive service agreements and responsive customer support not only enhance operational efficiency but also foster a collaborative environment for innovation, ensuring that manufacturers are equipped to handle evolving technological demands.




„Thanks to the LUVIR technology, the solder resist process could be switched directly from the previously used mask exposure to direct exposure. As an outstanding digital solution on the market, this technology has been able to demonstrate fast process times and superior quality on our certified conventional ink in production. This allowed us to fully digitize the solder mask process at low cost – without process or ink adjustments. An excellent benefit to our production in Rot am See.“
Ralf Göhringer (Head of Production WE Rot am See)
I would definitely recommend the Limata machine and team for a future company purchase
Michael Greenaway
Compunetics Inc.
“The Limata ldi has been amazing!! Best thing we did was buy this machine”
Richard Brady
GM
Circuitlabs
“Since 2019, we have been running the Limata X1000 LDI system (including LUVIR for solder mask imaging) in daily production as an addition to our current process with film. The machine was capable of properly exposing Taiyo PSR-4000 BN (DI) solder mask types on normal to high-copper boards using a new and unique direct imaging process. The machine operating interface is very user friendly which allowed for a quick technical training curve. The pre-registration processing reduced several seconds of production time at every print. Limata support and service staff is incomparable. They supported our team every step of the way at basically any time of the day or night, with literally, an immediate response time, customizing the software interface to best fit our Operations and needs.
We have exposed more than 8,000 prints since end of October, on various solder mask colors and some resist film panels. Limata, has proven to be very capable and innovative. They are a strong contender in the industry.
We have very much enjoyed this project, and working with the team!
Thank you Limata for the continued support and being a part of our growth.”
Bill Sezate
Vice President, GM
Summit Interconnect
As a replacement to our current contact exposure process with film, the LIMATA X2000 system including LUVIR-Technology was capable of properly exposing non-LDI solder mask types using a direct imaging process. The machine offers cutting edge software with a very intuitive operating interface which allowed for quick technician training curve. The dual drawer system combined with pre-registration processing reduced several seconds of production time at every machine cycle. Limata support and service staff is world class. They added software patches to keep production running at shortest possible response times, customized the software interface to best fit our in-house Operations system, and even wrote a step-by-step machine processing manual. As a result of the project, we have exposed more than 16,000 times on various product types and solder mask brands/colors. Limata, in a very short timeframe as a company, has definitely shown they are truly innovative and will be challenging the industry of direct imaging for the top spot.
Kevin Beattie
Process Engineer
TTM Technologies
Forest Grove Division